Glass Marking
Laser를 이용하여 Glass Making을 하기는 쉽지 않습니다. 대부분의 Co2 Laser 경우는 조각면이 아주 거칠어지고(유리 particle 이 깨져 나오는 현상) 두께가 1mm 이하인 경우에는 거의 작업이 불가능 하며 유리 전체가 깨지는 현상이 발생 합니다. 이를 개선하기 위하여 사용하는 방법은 Thermal Effect 가 최소화 될수 있는 UV Laser를 활용 하면 가능 하게 됩니다. 기존 스마트폰의 강화유리 에도 마킹이 가능 하며 바코드등의 ID Printing 도 가능 합니다.

MOPA Laser Marking

UV Laser Marking
HIgh Peak Energy IR Laser Cutting
Glass Cutting
| Cutting method | Principle | Advantage | Shortcoming | |
| Traditional
method |
Mechanical cutting | Use a diamond or hard metal wheel to score lines, then break the glass mechanically |
Simple process and low cost | It is easy to cause waste of materials, and post¬ processing such as cleaning and polishing must be carried out after cutting. The cut surface is relatively rough and there are fine cracks. |
| Crack control method (YAG+CO2) |
A low-power laser is used to defocus the surface of the substrate to heat it. Due to the strong absorption of the laser by the glass, the local heat rises sharply to generate thermal stress, and then it is quenched to crack along the laser scanning path under the action of stress to separate the plate. |
Non-contact, non-polluting environment, easy to control |
Thermal impact is unavoidable, and in many applications, the cutting edge still needs to be ground, and the application scenarios are limited. |
|
| Melt evaporation cutting(High power CO2) |
Taking advantage of the good plasticity and ductility of the glass at the softening temperature, the focused laser is irradiated on the surface of the softened glass, and the high energy density causes the glass to melt, and then the molten glass is blown away by the airflow, resulting in grooves. Enables fusion cutting of glass. |
Avoid thermal stress | The cut is relatively rough, the glass is easy to burst, and the heat impact is unavoidable. |
|
| Laser cutting | Ultrafast laser cutting | The ultra-high-density laser beam generates self-focusing inside the glass, forming micron-scale wire holes in the material, and generating micro¬ cracks along the diameter direction by optimizing the spacing of the wire holes, and then applying external force to break the glass along the micro¬ cracks. |
High precision and no micro cracks, good cutting quality |
High cost, slow efficiency, and limited application fields. |
| Green laser cutting | The laser is focused on the lower surface of the glass, the focus moves from bottom to top, the laser pulse acts on the material point by point, and the laser focus moves quickly in space according to the predetermined design path to achieve material removal. |
Strong application ability | Low power, low efficiency, light pollution | |
| MOPA laser cutting | Similar to green light cutting, ordinary MOPA lasers cannot cut, and the peak value must be increased. |
Low cost, fast efficiency, strong application ability |
The edge chipping is relatively large, 200~500gm. | |
MOPA Laser Glass Cutting
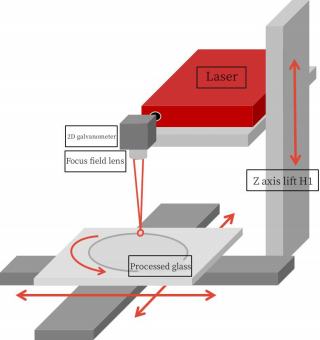
Core components of laser glass drilling equipment: Laser, Beam expander, Galvanometer, Field lens, control card, motorized Z-axis
Work principle: Laser pulses are focused on the bottom of the glass to create "micro-explosions" that break the glass into powdery particles.
Single-layer material removal is accomplished by scanning the laser focus horizontally. The material is removed layer by layer from below, and
finally the glass is perforated.
